Effective communication is important in educational settings, facilitating collaboration and productivity among teachers, students, and administrators.
Choosing between asynchronous and synchronous communication styles can make a big difference in how educational institutions operate and how well they achieve their goals.
While both methods let you share information, knowing which one suits your role best can help you work better.
In this article, we explain what asynchronous and synchronous communication is and talk about how they're different.
What is the Meaning of Asynchronous Communication?
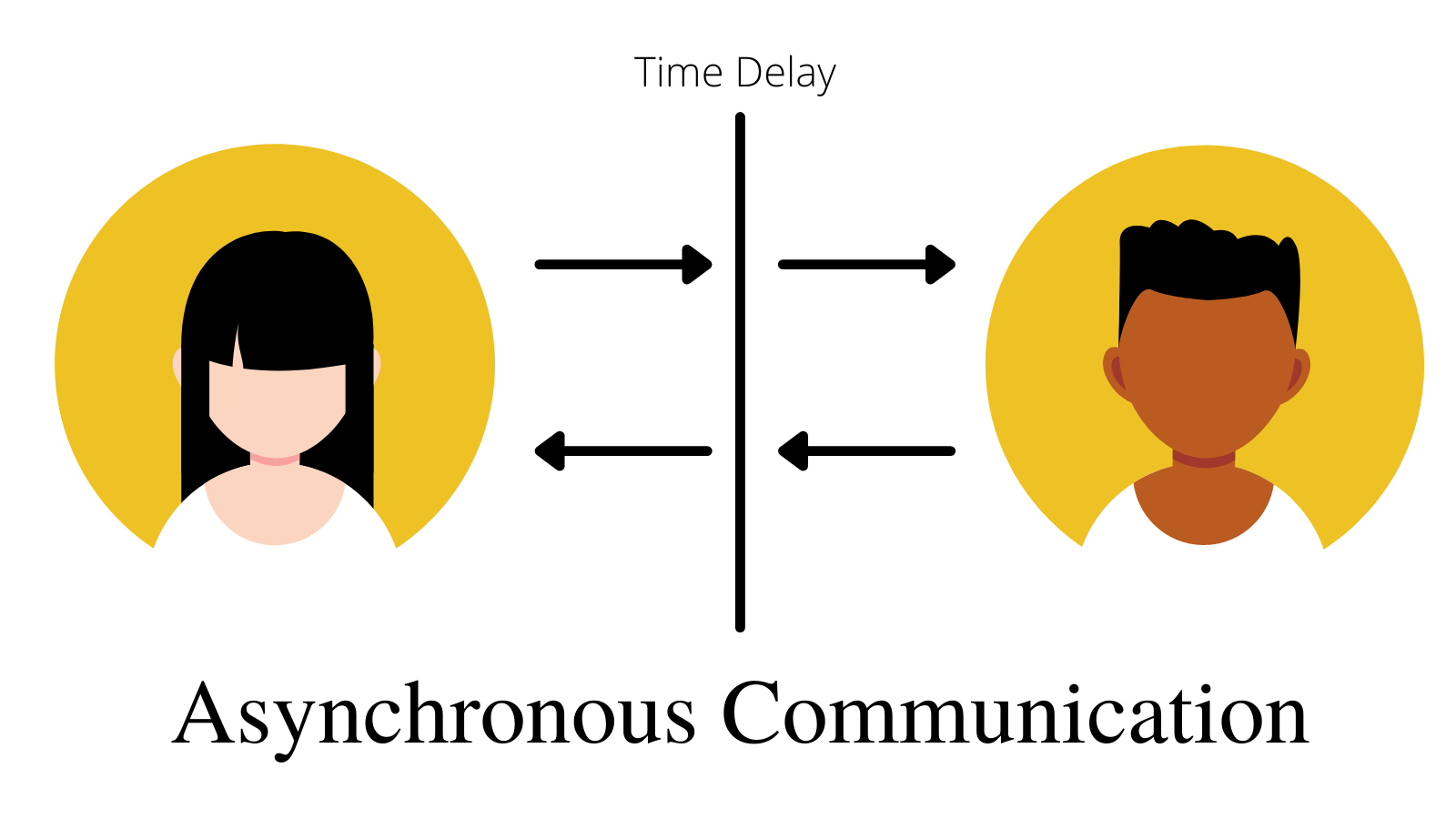
Asynchronous communication means communicating without needing an instant back-and-forth conversation. A classic example is email. With this method, there's no need to schedule meetings, and replies aren't urgent.
In this setup, instead of requiring everyone to be online simultaneously, you let team members choose when they work.
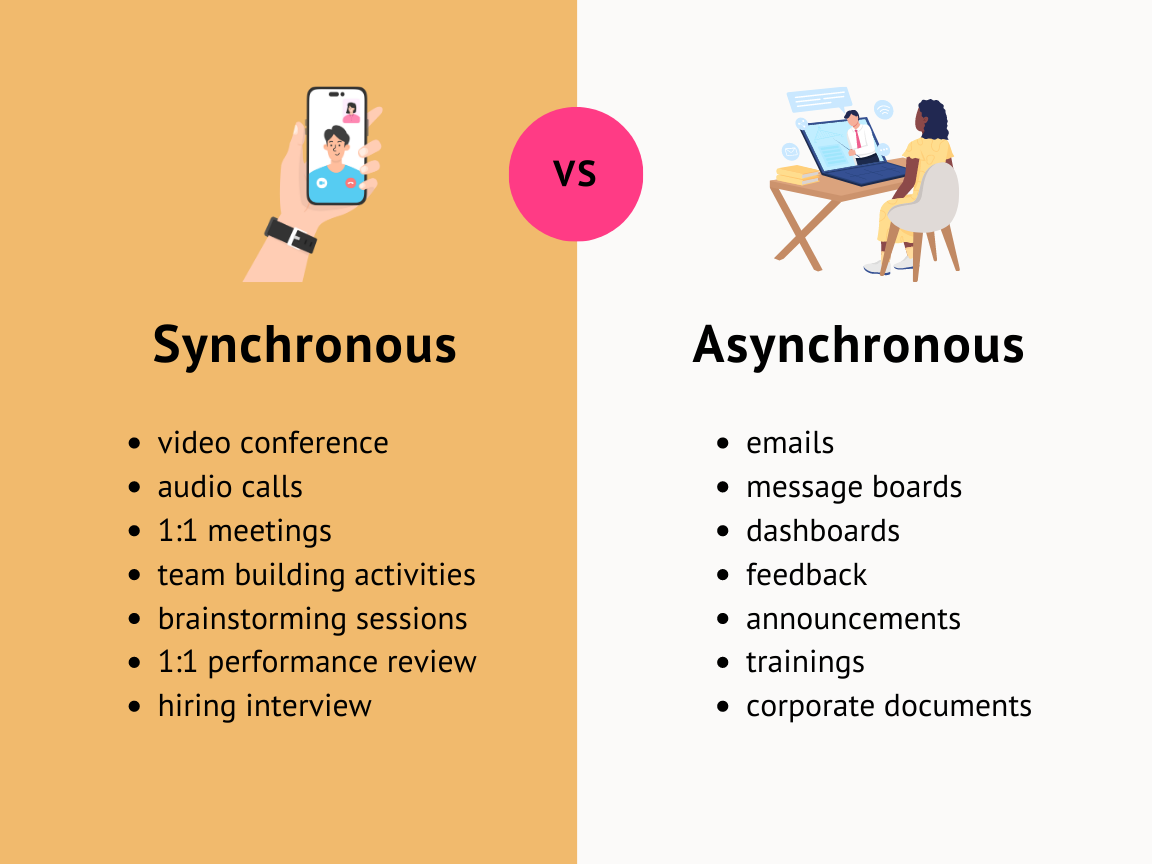
Examples of asynchronous communication:
Advantages of Asynchronous Communication
Asynchronous communication offers several benefits for educators, students, and administrators alike:
Flexibility
Participants can engage with course materials and discussions at their own pace, accommodating diverse learning styles and schedules.
Thoughtful Responses
Students have the opportunity to formulate well-thought-out responses, fostering deeper understanding and critical thinking.
Accessibility
Archived communication ensures that course materials and discussions remain accessible to all participants, promoting transparency and inclusivity.
Minimized Interruptions
Asynchronous communication reduces disruptions to learning, allowing students to focus on tasks without constant interruptions.
What is the Meaning of Synchronous Communication?
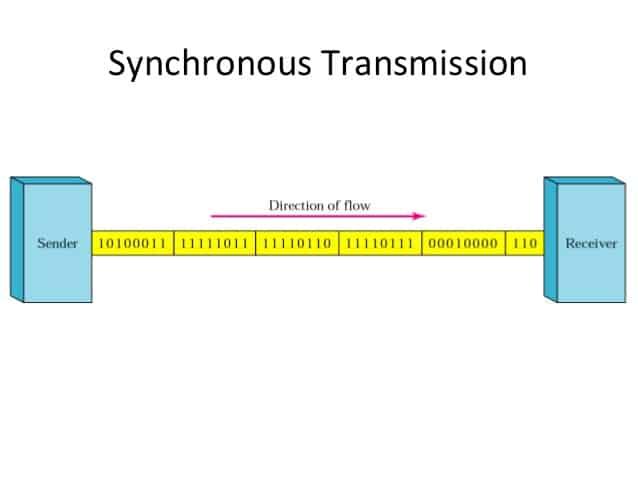
Synchronous communication happens in real time when everyone is online together. It allows for immediate responses. It's typical in physical places, where teachers can easily approach students for quick discussions.
Examples include,
Advantages of Synchronous Communication
Synchronous communication plays a crucial role in facilitating immediate interaction and engagement in educational environments:
Real-Time Collaboration
Students and teachers can engage in dynamic discussions, collaborative activities, and interactive learning experiences.
Immediate Feedback
In synchronous sessions, educators can provide instant feedback and clarification, enhancing student comprehension and learning outcomes.
Social Connection
Synchronous communication helps build a sense of community among participants, fostering peer support and collaboration.
Enhanced Instructor Presence
Live sessions allow educators to demonstrate enthusiasm, empathy, and expertise, creating a more engaging learning environment.
Synchronous Vs. Asynchronous – Differences
Here are some key differences between asynchronous and synchronous communication:
Delivery speed
Synchronous communication happens in real-time. On the other hand, asynchronous communication involves a delay between sending and receiving messages.
Length of discussions
Synchronous communication allows for longer discussions, like in online meetings. On the contrary, asynchronous communication demands clear, concise messages.
Response timing
In synchronous communication, immediate responses are expected. But in asynchronous communication, replies can wait, suiting tasks that don't need urgent feedback.
Flexibility
Asynchronous communication offers more flexibility since there's no pressure to reply immediately. This allows for better-quality responses and increased productivity. Synchronous communication requires timely participation, often during live lectures.
Asynchronous vs Synchronous - Which is Right for You?

The truth is, there's no one-size-fits-all answer to this question. A balanced mix of both asynchronous and synchronous communication usually works best for most educational institutions. Relying solely on one or the other isn't typically effective.
Consider the following factors when selecting the appropriate communication method:
Consider your audience
In educational environments, understanding the characteristics of your audience is essential. Factors such as generational disparities, personality traits, introversion versus extroversion, and the size of the audience can significantly influence the effectiveness of synchronous or asynchronous communication.
For instance, older educators may prefer synchronous lectures, while younger students may find recorded video lectures more engaging and accessible.
Complexity of the message
Assess the complexity of the information you need to communicate and select the most appropriate method accordingly. While synchronous communication has traditionally been favored for conveying complex messages, advancements in technology have made asynchronous communication equally effective.
Determine whether the content requires immediate interaction and feedback or if it can be effectively conveyed asynchronously, allowing participants to digest the information at their own pace.
Urgency of communication
Timing plays a crucial role in determining the suitable communication method within educational settings. Urgent matters may demand immediate responses, making synchronous methods such as live discussions or video conferencing more appropriate.
Conversely, less time-sensitive tasks can be managed asynchronously, such as exchanging documents or engaging in discussions via online platforms, enabling participants to respond at their convenience without disrupting their schedules.
 icons at the top right corner of the subsection.
icons at the top right corner of the subsection.